It’s up to hunters to comply with new regulations on moving deer carcasses and using mineral lures—but it’s worth it to stop the spread of CWD
The Boone & Crockett Club, North America’s oldest wildlife and habitat conservation organization founded by Theodore Roosevelt himself, recently made a bold recommendation to end all human-assisted live transport of deer and elk. Based on the most recent science, B&C said this is absolutely necessary to prevent unknowingly relocating animals infected with chronic wasting disease. Without a practical test for CWD in live animals, the risk is just too great, especially when you consider the rapid spread of the disease in recent years.
CWD has made headline news in the past 12 months—either because the disease has spread or because new regulations are being rolled out to slow the epidemic. We recently counted seven states where chronic wasting disease has deepened its grip since the fall 2018 opener. And we collected news stories from 25 states in the past year that have asked hunters or deer farms to follow new rules meant to control the disease.
Here’s what this means for your hunting.
You May Not Be Able to Bring Deer Carcasses Across State Lines
The recent wave of enhanced regulations leaves only a few states without some kind of official ban on transporting deer carcasses. If moving live deer and elk is too great a risk, many hunters probably recognize that we move just as many dead deer before testing them for CWD.
As a result, 16 states have made recent changes to prevent hunters from bringing home parts of deer harvested in CWD-positive states—or anywhere outside state lines. For a full look at import bans across the country see the map below.
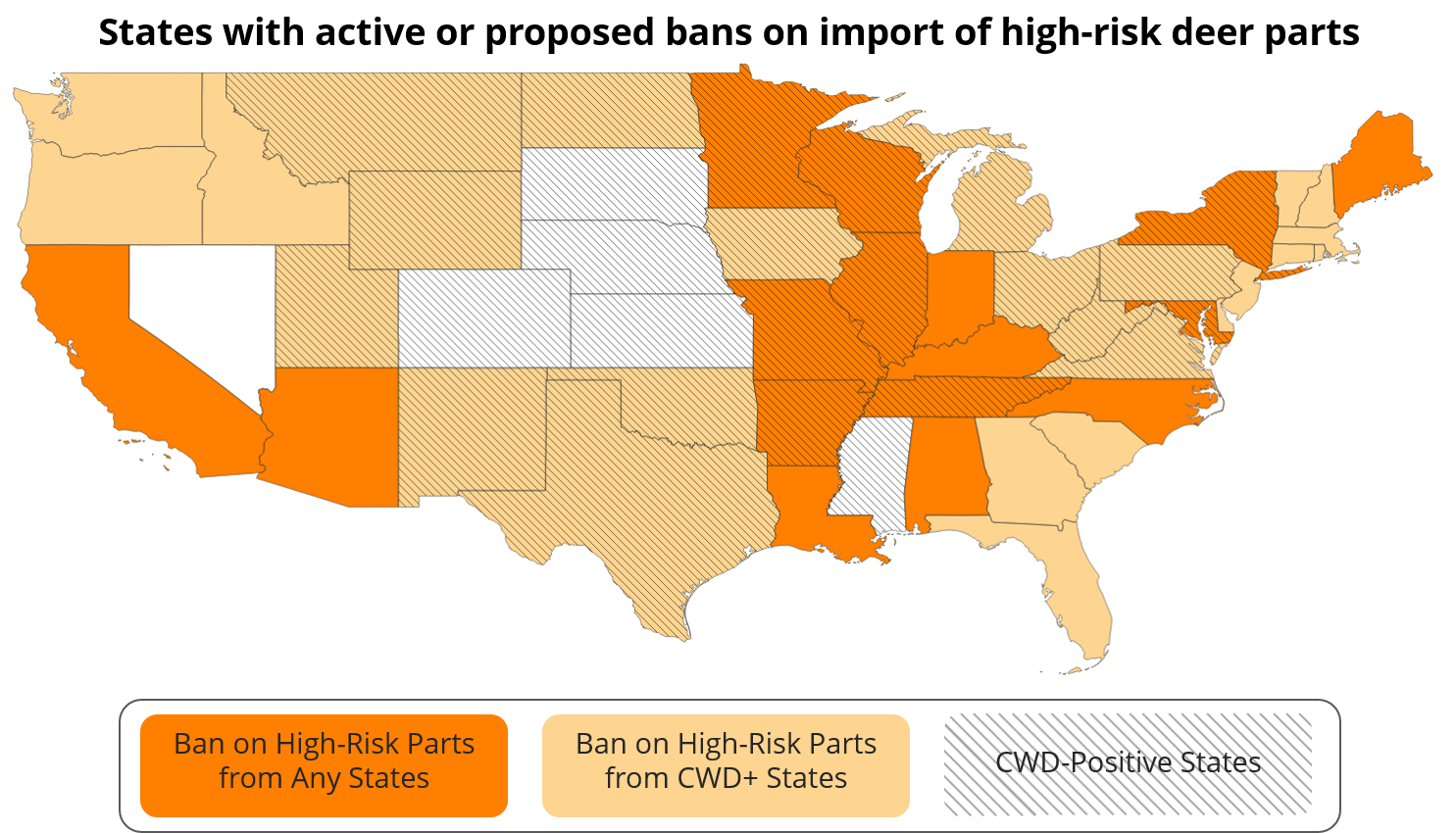
For example, in Oklahoma, where hunters contribute $680 million annually to the state’s economy, the Department of Wildlife has proposed new rules dealing with the import, transportation, or possession of deer carcasses and live deer. The state is surrounded by CWD-positive areas in Texas, New Mexico, Colorado, Kansas, Missouri, and Arkansas.
The Carolinas now have strict guidelines on which parts of deer, moose, and elk can be brought home. Their neighbor Tennessee discovered its first CWD-positive deer in 2018.
And Kentucky recently expanded its ban on deer imports to include all U.S. states—regardless of whether CWD has been detected there. Policies like this often link strongly to two factors: the long “incubation” period of the disease and the general lack of research on all the ways it spreads.
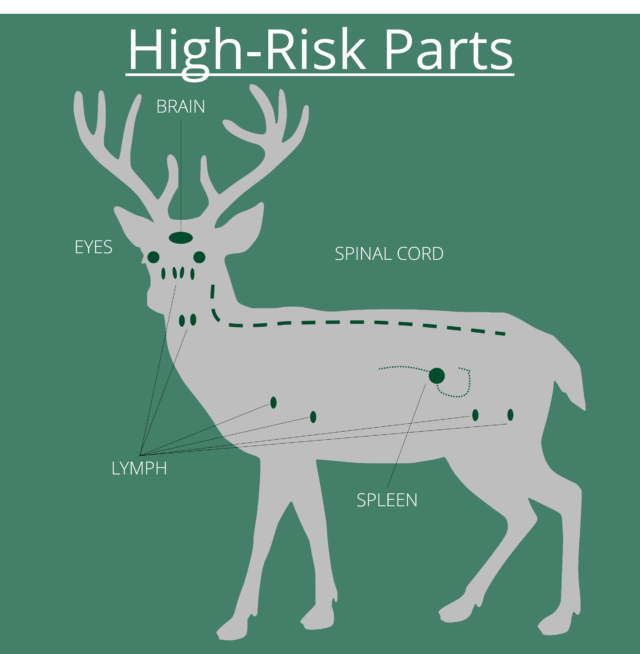
At issue are the “high-risk” parts of the deer, which house the animal’s central nervous system. This is where CWD prions would be highly concentrated. Some states, like Kansas, have opted to educate hunters and urge them not to transport anything but deboned meat, cleaned skulls, finished taxidermy, or tanned hides—but stop short of regulating the practice.
Now it’s on sportsmen and women to step up on our own.
CWD Testing May Not Be Optional
Hunters voluntarily submitting deer samples has been the backbone of many CWD surveillance efforts for years. The disease has become such a concern, though, that some states have implemented mandatory testing in vulnerable or infected areas. In designated areas, hunters are required to submit a high-risk part, like the lymph nodes, for testing by the state wildlife agency.
This is part of what Indiana is preparing to do in the event that CWD spreads from either Illinois or Michigan. Mandatory testing and culling deer in infected areas are key parts of the state’s CWD response plan. But those measures, especially mass culling, comes with a steep price: The economic impact of lost hunting opportunities is a major concern for the state’s $15.7-billion outdoor recreation industry.
With wildlife managers still gathering samples in Tennessee’s new outbreak area, Alabama Department of Conservation and Natural Resources has expanded its surveillance efforts. More harvested deer are being sampled and tested in counties bordering Mississippi and Tenn, but there have been no positive cases of CWD in Alabama, so far.

Deer Farms Will Be Under Increased Scrutiny
Deer farm restrictions are being considered by more states as the managers of our wild herds work to keep the captive deer industry accountable. Minnesota, New York, Tennessee, and Wisconsin all took up proposals or instituted new restrictions on captive deer farms in 2018.
In Minnesota, legislation has been proposed that would increase the containment requirements for captive deer farms. They are likely looking at neighboring Wisconsin, a stronghold for both the disease and the deer farming industry, and hoping to avoid the same fate.
Expect Broad Changes in the Coming Years
After the year CWD has had, sportsmen and women should expect that this disease will change the way we hunt. But there’s still time to adapt to relatively small concessions—whether it’s mandatory testing, restrictions on certain lures, or extra time in the woods to prepare your harvested animal for safe transport—to help control this epidemic.
The stakes are high, and how we respond could mean the difference between carrying on our deer hunting traditions and watching the decline of our wild deer herds.
Top photo by Michigan DNR via flickr








































![Air gun 101: The differences between .177 & .22 – Which jobs they do best ? [Infographic]](https://airgunmaniac.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/g44-150x150.jpg)


