Albino and leucistic deer are two distinct genetic conditions that affect the coloration of these magnificent creatures. While both conditions result in a lack of pigmentation, albino deer exhibit a complete absence of melanin, causing their fur, skin, and eyes to appear pure white. On the other hand, leucistic deer retain some pigment, resulting in a paler or patchy coloration. Understanding the differences between these fascinating phenomena is crucial in appreciating the unique beauty and biology of these rare deer species.
Understanding the Distinction: Albino vs Leucistic Deer
Albino and leucistic deer are two different conditions that affect the pigmentation of these animals. Albino deer have a complete lack of melanin pigment in their fur, skin, and eyes due to the absence of a specific enzyme called tyrosinase. This enzyme is responsible for producing melanin, which gives color to the hair, skin, and eyes. Without it, albino deer appear completely white or very pale with pink or red eyes.
On the other hand, leucistic deer have a lack of melanin pigment only in some areas of their body. This condition is caused by the absence of melanin-producing cells in those specific areas. As a result, leucistic deer may have patches or spots of white or light-colored fur amidst their normal-colored fur. Unlike albino deer, leucistic individuals typically retain normal eye color.
It’s important to note that both albino and leucistic deer are genetic conditions that can be inherited. However, progressive greying, as mentioned in the previous article about birds, is not considered a heritable condition. Progressive greying refers to the gradual loss of pigmentation in an individual’s feathers or fur over time.
In conclusion, while albino deer have a complete lack of melanin throughout their bodies due to the absence of tyrosinase enzyme, leucistic deer only have a partial lack of melanin in certain areas caused by the absence of melanin-producing cells. Understanding these distinctions helps us appreciate the unique characteristics and challenges faced by these fascinating animals.
Decoding the Variations: Albino or Leucistic Deer?

Albino Deer
Albino deer are characterized by a complete lack of melanin pigment, which gives them a pure white appearance. This is caused by the absence of a specific enzyme called tyrosinase, which is responsible for producing melanin. As a result, albino deer have pink eyes and nose, as well as white fur. Albinoism is a genetic condition that is inherited from both parents.
Leucistic Deer
Leucistic deer, on the other hand, have a different variation in their pigmentation. Leucism is the lack of melanin pigment in some feathers or fur due to the absence of melanin-producing cells. Unlike albino deer, leucistic deer may still have some pigmented areas on their body, such as patches or spots. These areas can vary in color and can range from light brown to pale yellow. Leucism can also affect other animals and birds.
Differences between Albino and Leucistic Deer
1. Pigmentation: Albino deer have completely white fur with no pigmented areas, while leucistic deer may have patches or spots of pigmented fur.
2. Eyes and Nose: Albino deer have pink eyes and nose due to the absence of melanin, while leucistic deer may have normal-colored eyes and nose.
3. Genetic Inheritance: Albinoism is a genetic condition that is inherited from both parents, while leucism can occur spontaneously without any genetic basis.
4. Randomness: The white fur in albino deer is evenly distributed throughout their body, while leucistic deer may have a more random pattern of white patches or spots.
It’s important to note that both albino and leucistic deer may face challenges in the wild due to their unique pigmentation. They may be more visible to predators or have difficulties blending into their surroundings. Conservation efforts are important to ensure the survival of these unique individuals and maintain biodiversity.
Differentiating Between Albino and Leucistic Deer: A Closer Look
Albino and leucistic deer are often mistaken for each other due to their similar appearance, but there are distinct differences between the two conditions.
Albino Deer:
– Albino deer have a complete absence of melanin pigment in their fur, skin, and eyes. This is caused by the absence of a specific enzyme called tyrosinase.
– The lack of melanin results in a pure white appearance, with pink or light-colored eyes and hooves.
– Albino deer are extremely rare and have a higher susceptibility to sunburn and other skin-related issues due to their lack of protective pigmentation.
– Their vision may also be impaired as the absence of melanin affects the development of the optic nerve.
Leucistic Deer:
– Leucism is characterized by the partial loss of melanin pigment in an animal’s fur, feathers, or skin. It is caused by the absence or malfunctioning of melanin-producing cells.
– Leucistic deer may exhibit patches or streaks of white or light-colored fur amidst their normal colored fur. These patches can be irregularly distributed across their body.
– Unlike albino deer, leucistic individuals retain some pigmentation in their eyes and hooves. Their eyes may appear lighter than usual but not pink or red like in albinos.
– Leucism does not typically affect an animal’s health or survival as severely as albinism does.
It is important to note that both albino and leucistic deer face challenges in their natural habitats due to their unique coloration. They may stand out more to predators or have difficulty blending into their surroundings during hunting seasons.
Understanding these differences between albino and leucistic deer can help wildlife enthusiasts and researchers accurately identify these individuals and contribute to their conservation efforts.
Exploring the Contrast: Albino versus Leucistic Deer
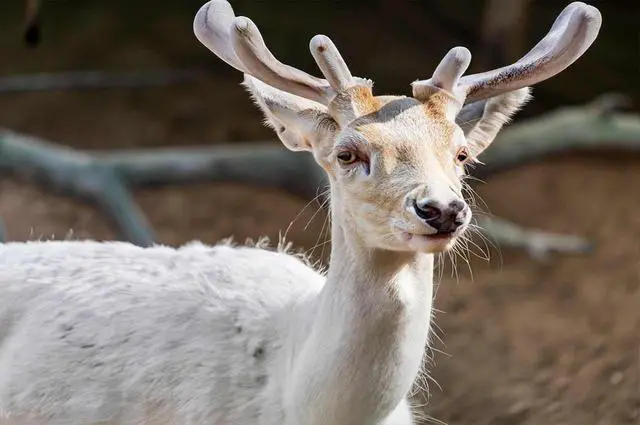

Albinism and leucism are two conditions that can affect deer, resulting in a striking contrast in their appearance. While both conditions involve a lack of pigmentation, there are key differences between them.
Albinism:
Albinism is a genetic condition characterized by the complete absence of melanin pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes of an animal. This is due to the absence of a specific enzyme called tyrosinase, which is responsible for producing melanin. As a result, albino deer have completely white fur, pink eyes, and pale hooves. They lack any form of pigmentation and appear almost ghostly.
Leucism:
Leucism, on the other hand, is caused by a lack of melanin-producing cells in certain areas of the body. Unlike albinos, leucistic deer still have some pigment present in their bodies. However, this pigmentation may be reduced or diluted, resulting in lighter-colored fur or patches of white on their bodies. Leucistic deer often have normal-colored eyes and hooves, distinguishing them from albinos.
It’s important to note that neither albinism nor leucism affects the health or behavior of deer. These conditions are purely cosmetic and do not impact their survival in the wild.
In conclusion, while both albino and leucistic deer exhibit a lack of pigmentation, albino deer have a complete absence of melanin while leucistic deer retain some level of pigmentation. Understanding these differences helps us appreciate the unique beauty found in nature’s variations.
Unraveling the Mystery: How to Tell Albino and Leucistic Deer Apart

Albino and leucistic deer may appear similar at first glance, but there are distinct differences between the two. Albino deer have a complete lack of melanin pigment in their fur, which gives them a pure white appearance. This is due to the absence of a specific enzyme called tyrosinase that is responsible for producing melanin. In contrast, leucistic deer have a partial loss of melanin pigment, resulting in patches of white or light-colored fur.
Distinguishing Features
One way to tell albino and leucistic deer apart is by looking at their eyes. Albino deer have pink or red eyes due to the lack of pigmentation in their irises. In contrast, leucistic deer typically have normal-colored eyes.
Another distinguishing feature is the pattern of coloration on their bodies. Albino deer often exhibit a completely white coat with no spots or markings. Leucistic deer, on the other hand, may have patches of white or light-colored fur interspersed with areas of normal pigmentation.
Causes and Heritability
The causes of albinism and leucism in deer are not fully understood. Albinism is believed to be caused by a genetic mutation that affects the production of melanin. It is a heritable condition that can be passed down from parent to offspring.
Leucism, on the other hand, can occur as a result of various factors such as genetic mutations or environmental influences during development. It is not always heritable and can occur sporadically in individual deer.
In conclusion, while albino and leucistic deer may share similarities in their appearance, there are key differences that can help distinguish between the two. Understanding these differences can contribute to our knowledge and appreciation of these unique genetic variations in the deer population.
Albino or Leucistic? Understanding the Differences in Deer
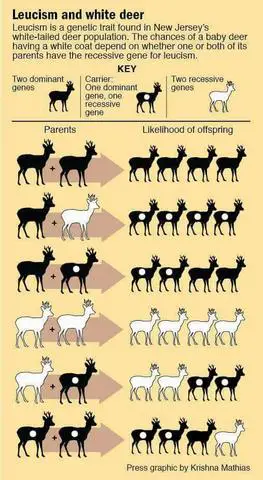
Albinism in Deer
Albinism is a genetic condition that results in the complete absence of melanin pigment in an organism. In deer, this means that their fur, skin, and even their eyes lack any coloration. Albino deer have a pure white appearance and often have pink or red eyes due to the lack of pigmentation. The absence of melanin-producing cells, specifically the enzyme tyrosinase, is responsible for albinism in deer.
Leucism in Deer
Leucism, on the other hand, is a different condition that affects the pigmentation of deer. Unlike albinism, leucistic deer still have some melanin pigment present in their bodies. However, they lack the ability to produce normal amounts of melanin due to a reduction or absence of melanocytes (melanin-producing cells). This results in a partial loss of coloration and can cause patches or areas of white or light-colored fur on the deer’s body.
Distinguishing Features
One way to differentiate between albino and leucistic deer is by looking at their eye color. Albino deer have pink or red eyes due to the absence of pigmentation in their irises. Leucistic deer, on the other hand, usually have normal-colored eyes since they still possess some melanin pigment.
Another distinguishing feature is the pattern of color loss. In albino deer, the entire body lacks pigmentation uniformly, giving them an overall white appearance. Leucistic deer often exhibit a more patchy distribution of color loss, with areas of white or light-colored fur mixed with normal-colored fur.
It’s important to note that both albino and leucistic deer are relatively rare occurrences in nature. These conditions can make the affected deer more susceptible to predation due to their lack of camouflage. However, they also hold a certain fascination for wildlife enthusiasts and photographers who appreciate their unique appearance.
In conclusion, while both albino and leucistic deer display a lack of pigmentation, there are key differences between the two. Albino deer have a complete absence of melanin, resulting in white fur, pink eyes, and hooves. On the other hand, leucistic deer have reduced pigmentation but may retain some coloration in their eyes, fur, or hooves. Understanding these distinctions can help us appreciate and protect these unique creatures in their natural habitats.











































