So, you have a flat tire or one that’s leaking air. It’s not the end of the world. Luckily there are safe and cost-effective ways to properly repair most tire punctures. The purpose of this article is to show you the difference between a safe, permanent repair and a temporary string, plug or patch repair.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHSTA) and the Tire Industry Association (TIA), the only method to properly repair a tire puncture is to fill the injury with a repair stem and back the stem with a repair patch. This is commonly known as a combination repair or a patch/plug repair.
 Patch/plug repairs are most often performed using a one-piece repair unit that combines the repair stem and cap (or patch) into one unit. However, special circumstances may require the use of a two-piece combination repair (ex. If the angle of the puncture exceeds 35 degrees). The repair is then permanently bonded to the inside of tire and through the injury channel using a cold, chemical vulcanizing process. The repair essentially becomes part of the tire, creating an air-tight seal that keeps air in and moisture and contaminants out (more on this procedure below).
Patch/plug repairs are most often performed using a one-piece repair unit that combines the repair stem and cap (or patch) into one unit. However, special circumstances may require the use of a two-piece combination repair (ex. If the angle of the puncture exceeds 35 degrees). The repair is then permanently bonded to the inside of tire and through the injury channel using a cold, chemical vulcanizing process. The repair essentially becomes part of the tire, creating an air-tight seal that keeps air in and moisture and contaminants out (more on this procedure below).
Tire Plugs and String Repairs are Temporary Repairs
Emergency roadside plug repairs are NOT intended to be a permanent tire repair. Plugs and string repairs are designed to get you back up and rolling long enough to get home or to the nearest service center to perform a proper tire repair.
The common misconception with plug and string repairs is that because they hold air, they are safe to use. While it is true that many plug repairs do a great job of keeping air in the tire, that’s only part of the equation. Because they’re not completely sealing the injury, plug repairs may allow air and moisture to penetrate the body of the tire. Over time, this could lead to a dangerous (or even deadly) blowout.
A Patch-Only Tire Repair Leaves Your Tire Susceptible to Damage
A tire repair that uses only a patch is also NOT considered proper or safe. A properly installed patch will do a great job of allowing the tire to hold air. However, similarly to the plug-only repair, the patch does not fill the injury channel. Therefore, air and moisture could seep into the tire from the tread surface and eventually damage the tire.
The Proper Tire Repair Process According to Industry Guidelines
 Only a proper patch/plug repair completely seals the puncture from inside the tire and through the entire injury channel. There are a few extra steps necessary to perform a proper tire repair in accordance with industry guidelines. We’ve developed a simple acronym to help organize and remember the steps: R.E.P.A.I.R.
Only a proper patch/plug repair completely seals the puncture from inside the tire and through the entire injury channel. There are a few extra steps necessary to perform a proper tire repair in accordance with industry guidelines. We’ve developed a simple acronym to help organize and remember the steps: R.E.P.A.I.R.
- Remove: To begin, the tire must be removed from the wheel assembly. This allows for a thorough inspection of both the inside and outside of the tire.
- Evaluate: With the tire removed from the rim, the puncture can be thoroughly evaluated to determine the size and angle of the injury. It can also be determined if the puncture did any significant damage to the cords or belts.
- Prepare: Once the tire has been determined to be in good enough condition to repair, it is time to prep the rubber surfaces to remove any damage and contamination to allow for maximum repair unit adhesion. First, the injury is drilled out using a carbide cutter to strip away and damaged cords or belts. Next, the inner liner is cleaned and buffed to a slightly rough texture. This also helps maximize adhesion of the patch/plug repair.
- Apply: The next step is to apply vulcanizing fluid through the injury and to the buffed area of the inner liner. It is then allowed to air dry for 5-10 minutes.
- Install: The one- or two-piece repair is installed through the injury channel and the patch portion is thoroughly stitched to the inner liner using a tire stitcher to completely push out any air that may have gotten trapped under the repair. The over-buffed area of the inner liner is treated with a thin layer of rubber sealant, and the excess repair is trimmed to approximately ¼” above the tread surface.
- Return to Service: The tire is now ready to be remounted to the rim, inflated, balanced and mounted back on the vehicle.
When is it Safe to Repair Your Tire?
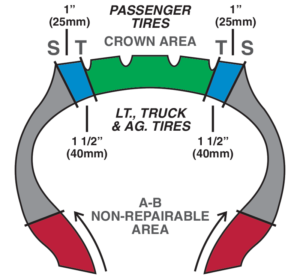 There are a number of factors that may determine whether or not your tire is safe to repair. These factors fall into three main categories:
There are a number of factors that may determine whether or not your tire is safe to repair. These factors fall into three main categories:
- Placement of the Injury: For passenger tires, puncture repairs must be within the crown area of the tire. Damage to the shoulder or sidewall cannot be repaired.
- Size of the Puncture: For fabric-ply passenger and light truck tires, the maximum repairable injury size is ¼” (6mm). For steel belted light truck, medium and heavy-duty truck tires, the maximum injury size is 3/8” (10mm).
- Overall Condition of the Tire: The condition of your tire may determine whether it is safe to repair. Excessive wear, casing separation, impact damage and other conditions may make it unsafe to properly repair your tire. For a more comprehensive list of repairable vs. non-repairable conditions visit our blog Can Your Tire Be Repaired?
Conclusion:
The occasional flat or leaky tire is an unavoidable part of life. But, taking shortcuts to repair it can be dangerous to you and your passengers. Take the time and do the research to do the job right and/or find a reputable tire repair shop trained in proper tire repair procedure.







